California Management Review
California Management Review is a premier academic management journal published at UC Berkeley
by Vaneet Kaur

“Without industry and frugality, nothing will do, and with them everything.” ― Benjamin Franklin
The pandemonium caused by pandemic is neoteric to the corporate world, still and all, but the ingredients for concocting an elixir for enterprises plagued by COVID-19 may already be in the land of the living. Leaders have often settled on frugality as a way of securing their businesses during times of uncertainty. Could frugality hold the potential to pivot organizations out of this particular state of virus-related snafu?
The answer is affirmative and at the same time fragmentary. The credo of frugality is cardinal to this effervescent enigma and tapping into it can potentially give rise to springheads of supplements. In the words of Jeff Bezos, “Frugality drives innovation, just like other constraints do. One of the only ways to get out of a tight box is to invent your way out.” Thus, frugal mindset is essentially a substratum, however, innovations emanating from it – Frugal Innovations – can serve as gateways to success.
Frugal innovation is defined as the agile art of ingeniously simplifying and repurposing existing products and assets to serve a higher purpose. The concept has been linked to notions like that of “Jugaad” in India and “Jeitinho” in Brazil, which as often as not entail evocation to renderings with makeshift tools and technologies, in order to creatively solve critical socioeconomic problems on a shoestring.
In sooth, frugal innovation can be deemed as a metaparadigm, which engenders an entirely novel way of thinking about innovation and value creation. It can be equated to ‘affordable excellence’ since the essence of this ideology lies in doing more with less. It is characterized by affordability, agility, and speed - which is antithesis of usual practices of innovation in developed economies that draw heavily from state-of-the-art R&D labs, hefty budgets, and rigid go-to-market processes. Thus, the need for making such a strategic approach all-pervading accentuates when the world economy is getting decimated by coronavirus and its concomitants.
Organizations worldwide need to make a paradigm shift to not only survive during the current crisis but also to thrive in the recessionary post-coronavirus world – a stark new world where cost-conscious customers will continually seek more value for less. Coronavirus has bedeviled the firmament with not only uncertainty about availability of certain resources but also with a general scarcity of many resources. Even in these times, it is important to remember that having less does not necessarily mean being less. In situations when organizations need to flex existing resources, employees are challenged to step outside of the scarcity mindset and leverage existing resources, thereby ensuring optimum utilization of organizational resources.
Against this backdrop, development of creative attitudes to get around challenges can usher the industry towards a pathway to untie the Gordian knot. As it happens, in frugal environments, organizations compensate for the lack of resources by drawing heavily on their internal and external stock of knowledge as well as learning capabilities. In the age of coronavirus, problems are essentially compounded - therefore, the embryonic catholicon can be brewed by coalescing strapping strategic solutions in the making. Salient stratagems proffer development of Knowledge-Based Dynamic Capabilities as panacea to pandemic. These meta capabilities are formed by harnessing Knowledge Processes to build Higher-Order Dynamic Capabilities which equip organizations with instantaneous responsiveness to environmental dynamism.
Verily, a dyad of Knowledge-Based Dynamic Capabilities and Frugal Innovation can burgeon as the acme of modus operandi required to stay atop even amid a pandemic. This ambidextrous approach holds the potential to produce synergistic effects, thereby sanguinely transmogrifying into a magic formula that can bestow organizations with a frugality-based advantage. Such an edge can help organizations to not only weather the corona superstorm but also build a COVID-19 legacy sturdily underpinned by superlative Knowledge-Based Dynamic Capabilities.
Figure 1: Idea in Brief

Frugality-based advantage is an advantage that a firm achieves over competitors in its ability to develop and use frugal innovations i.e. innovations that overcome external resource constraints. Based on different categories of constraints that a firm might encounter, frugality-based advantages can be classified into following three types:
Input frugality-based advantage: It can be derived by developing capabilities to generate innovations that address restrictions in the availability of inputs needed for a firm’s production process. At the time of pandemic, when struggles of procuring specific inputs are accentuated, scrounging for new ways of substituting scarce resources can prove to be highly beneficial for organizations.
Income frugality-based advantage: It can be derived by formulating strategies that solve limitations in consumers’ capacity to purchase and ply products. The economic consequences of coronavirus pandemic have meant worldwide steep declines in both personal income and consumer spending. Hence, a large group of consumers are looking for frugal solutions to be able to make ends meet.
Infrastructure frugality-based advantage: It can be derived by devising strategies that resolve constraints in hard and soft infrastructure. Firms must strive to come up with goods and services that are mostly self-contained in their operation so that production and distribution can remain incessant even in instances of unreliable infrastructure.
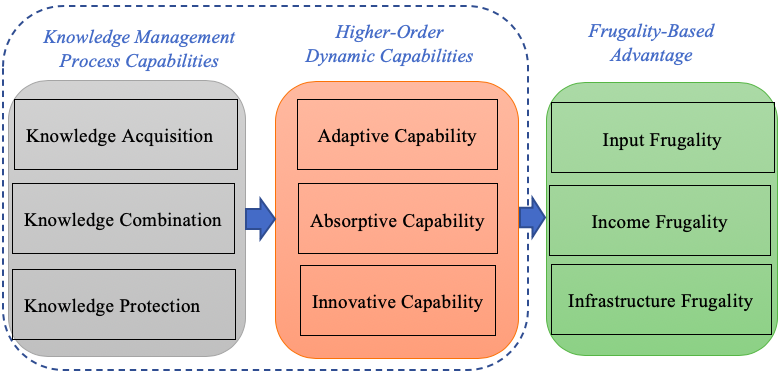
An organization striving to innovate frugally must utilize knowledge management and its related processes to learn about internal and external dynamics in an endeavor to adapt its systems and processes to befit the frugal framework. In doing so, organizations need to develop Knowledge Management Process Capabilities as the bedrock for erecting Higher-Order Dynamic Capabilities.
Knowledge Management Process Capabilities at the base level entail search for new external sources of knowledge as well as efficacious utilization of knowledge stored in organizational routines and standard operating procedures. The tripartite knowledge capabilities that can assist firms in their pursuit of frugal innovations are Knowledge Acquisition, Knowledge Combination and Knowledge Protection Capabilities.
Concurrently, Higher-Order Dynamic Capabilities are the abilities of an organization to utilize its idiosyncratic combinations of resources and processes to modify, integrate, and renew the organizational competencies. A triad of Adaptive Capability, Absorptive Capability, and Innovative Capability forms the comprehensive construct of Higher-Order Dynamic Capabilities.
Knowledge Management Process Capabilities as First-Order Capabilities provide a strong substructure for building Higher-Order Dynamic Capabilities. The former feed organizations with knowledge about emerging opportunities which serves as a desideratum in adaption of novel technologies, techniques and approaches and thus changing product-market scope. In a similar fashion, Knowledge Capabilities aid in the strengthening Absorptive Capabilities of an organization. Furthermore, if a firm is to be a system, knowledge is the input and innovation capability is the output of that system. Thus, Knowledge Management Process Capabilities underpin Higher Order Dynamic Capabilities of an organization and the tandem of both these levels of capabilities gives rise to superior Knowledge-Based Dynamic Capabilities.
While Knowledge-Based Dynamic Capabilities focus on leveraging knowledge resources to build Higher-Order Dynamic Capabilities, they can perfectly dovetail Frugality-based Advantage. When an organization is faced with external constraints, it can utilize its knowledge processes to absorb Valuable, Rare, Inimitable and Non-substitutable (VRIN) opportunities, adapt to altered conditions and frugally innovate, thereby systematically resolving constraints through more dynamic applications and adjustments of the firm’s resources and capabilities. Thus, even during times of extreme uncertainty, Knowledge-Based Dynamic Capabilities can strategically position an organization and help them develop a frugality-based competitive advantage.
Figure 2: Proposed Framework
To illustrate the mechanics of this model, let us take the case of Huazhu Group, a hospitality giant based in Shanghai that demonstrated how Knowledge-Based Dynamic Capabilities can become a pathway to success in a constrained environment. The company had set up a crisis task force that met every day to review new knowledge and brought into operation its internal app called Huatong, to disseminate up-to-date guidance for whole organizational chain. This facilitated quick adaptation of central guidance regarding disease conditions and necessary public health measures to local situations. Consequently, 9 out of 10 directly managed assets of group were re-opened and 98% of Huazhu’s hotel managers resumed operations in the month of February. The group then started offering its rooms for quarantine purposes and in two weeks, over 4,200 of the group’s hotels provided isolation services with a peak of more than 50,000 stays in one day.
In sum, Knowledge-Based Dynamic Capabilities present a cohesive solution for attaining a strategic advantage when organizations are faced with external constraints. These superior capabilities conjoined with frugal approach create new meta-paradigms where internal capabilities become vehicles to turn debilitating external challenges into growth opportunities, thus creating VRIN innovations that can outlive pandemic.