California Management Review
California Management Review is a premier professional management journal for practitioners published at UC Berkeley Haas School of Business.
Ananya Hadadi Raghavendra, Pradip Kumar Bala, and Arindam Mukherjee

Image Credit | krakenimages
In today’s constantly changing and interconnected commercial environment, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has become a fundamental aspect of responsible and sustainable business practices.1, 2 A study from McKinsey and Nielsen IQ found that products with CSR-related claims experienced a 28% cumulative growth over five years, compared to 20% for products without such claims.3 Another report by Net Positive highlighted that one-third of employees resigned due to a lack of corporate values, with nearly half of Gen Z and Millennials willing to accept a pay cut to work for value-aligned companies.4 Additionally, the CDP report showed that only 0.4% of companies have a transition plan for environmental targets, emphasizing the gap in actionable CSR commitments.5
“Strategically Leveraging Corporate Social Responsibility: A Corporate Branding Perspective” Christine Vallaster, Adam Lindgreen, and François Maon. Volume 54, Issue 3 “Entering Conscious Consumer Markets: Toward a New Generation of Sustainability Strategies” Boyd Cohen and Pablo Muñoz. Volume 59, Issue 4
CEOs, as the visible representatives of their organizations, are tasked with driving and effectively communicating CSR initiatives to a diverse stakeholder group.6 Their role as CSR communicators has become increasingly important as societal expectations for ethical business practices have grown. CEOs are now seen as influencers, affecting public opinion and investment decisions. A report from MovingWorlds highlights the necessity for executives and leaders to take accountability for achieving sustainability targets beyond mere acknowledgment.7 It emphasizes that sustainability should be treated as a strategic priority, requiring measurable KPIs for each business function’s contribution to the broader sustainability strategy. This report underscores the importance of integrating CSR into core business functions and the significant role CEOs play in this integration. Furthermore, a report by Boyden, Cananda asserts that implementation of effective CSR strategies requires CEOs to be better communicators and more informed, thereby enabling them to create stronger communities where corporate leaders also serve as community leaders.8 The report underscores the necessity for CEOs and the C-suite to be involved in CSR as they serve as the company’s cultural center and influence the entire stakeholder base’s attitude toward corporate responsibility.
The increasing demand for more accurate and measurable Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) practices is driving the adoption of analytics in the field of CSR. This includes better tracking of progress, statistics, and facts related to CSR initiatives. Therefore, data analytics emerges as a crucial tool in this landscape. Amidst the deluge of information, data analytics efficiently processes vast amounts of data, revealing trends and patterns that might otherwise be missed. As the stakeholder reactions and responses depend on the publicly available data and stakeholders tend to view CEO publicly produced data with respect, it is apparent to apply data analytics on publicly available CEO communication data.9 Recent research10 highlights how advanced data analysis methods can offer valuable insights into CEO communications about CSR. It provides a quantifiable way to evaluate the frequency, sentiment, and impact of CSR-related CEO communications. Data analytics also aid in aligning CSR efforts with global sustainability goals like the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).11, 12, 13
The internet plays a crucial role in enhancing the visibility and impact of CSR initiatives. It serves as a dynamic channel for transparent communication, allowing companies to broadcast their CSR goals, activities, and achievements to a broad audience.14 In this regard, company websites are considered the most credible sources for making CSR information publicly accessible. Social media platforms can be another effective medium. According to GlobalWebindex, eco-conscious consumers show a strong preference for using social media as their main source of information about companies’ sustainability efforts.11 Additionally, a study on Twitter communication in the CSR area indicates that companies, leaders, and influencers use Twitter to communicate their CSR initiatives, engage with the public, and respond to societal concerns.15 This finding highlights the evolving landscape of CSR communication and the importance of social media in engaging with stakeholders and improving CSR efforts.
The relevance of CEO communications on CSR and the applications of data analytics to it is evident from the aforementioned paragraphs. Yet research on application of data analytics in CSR is still in it’s nascent stages. Therefore, this article seeks to fill this gap by attempting to develop an integrative framework that examines various forms of CEO communications and explores how they can be analyzed using different data analytics techniques to produce business outcomes. By analyzing data, companies can identify which CSR initiatives are most effective, how they contribute to the company’s goals, and where improvements can be made. This kind of insight is invaluable for making data-driven decisions that align CSR efforts with business objectives. This framework helps researchers, analysts and academicians to gain insights as to which data analytic technique can be used in order to analyze CEO communications and make the most out of their corporate communications.
CEO CSR communication refers to the ways in which chief executives articulate and share their company’s efforts and commitments in Corporate Social Responsibility.16 This encompasses the strategies and activities a company undertakes to manage its environmental and social impacts and to contribute positively to society. The communication aspect involves how CEOs convey these initiatives, progress, and values to various stakeholders, including employees, investors, customers, and the broader community.
The CEO, as the organization’s figurehead, plays a vital role in defining its values and priorities. When CEOs actively engage in CSR communication, it sends a strong message to employees, stakeholders, and the broader public that these initiatives are deeply embedded in the company’s mission and culture. Such communication from the CEO can motivate employees by aligning them with the organization’s social and environmental objectives, thereby boosting engagement and productivity.
Additionally, CEO communication about CSR is essential for building and maintaining trust among various stakeholders, including customers, investors, and employees. Open and meaningful dialogue about CSR efforts by the CEO not only fosters trust but also protects the organization against reputational risks. In an era where corporate actions are closely monitored, the CEO’s role as a communicator is crucial in addressing concerns and demonstrating the company’s dedication to ethical practices.
The rise of digital communication has significantly transformed how CEOs communicate about CSR. Platforms like social media, corporate websites, and podcasts have broadened the reach of CSR messages, allowing CEOs to connect directly with a global audience and share updates and achievements in real time. This digital approach has made CSR information more accessible and has democratized stakeholder engagement.
Moreover, digital platforms for CSR communication enable two-way interactions, where CEOs can receive and respond to stakeholder feedback, fostering a collaborative environment around CSR initiatives. This interactive model helps align CSR programs more closely with stakeholder expectations and needs, enhancing their overall effectiveness.
Data analytics is the art and science of making sense of large volumes of data.17 It’s like unraveling the intricate threads of a complex tapestry to reveal patterns, insights, and hidden treasures within the data. Think of it as the detective work of the digital age, where data analysts act as investigators, searching for clues and connections that can help businesses make informed decisions.
In essence, data analytics involves collecting, processing, and interpreting data to extract valuable information. It’s about transforming raw data into actionable insights that can guide businesses in understanding trends, making predictions, and solving problems. Data analytics is a powerful tool that empowers organizations to uncover opportunities, optimize processes, and gain a competitive edge in today’s data-driven world.
Today, the importance of data analytics in dissecting and understanding CEO communication cannot be emphasized enough. CEO communication takes various forms, from traditional methods like speeches and interviews to the dynamic realm of social media interactions and email correspondence. The critical role of data analytics in this context lies in its ability to systematically collect, organize, and analyze this diverse and extensive dataset. This process enables us to extract valuable insights that were previously challenging to uncover.
Data analytics empowers researchers and organizations to dive deep into the intricacies of CEO communication. Through the application of advanced analytical techniques, it allows us to identify recurring patterns, sentiments, and trends within this wealth of information. As a result, data analytics provides decision-makers with a comprehensive understanding of how effective, impactful, and aligned CEO communication is with the broader organizational mission and stakeholder expectations.
Data analytics also plays a pivotal role in deciphering the effectiveness of CEO CSR communication across different channels. It allows organizations to gain insights into themes, sentiments, and the overall impact of their messaging. By systematically analyzing data, organizations can tailor their communication strategies to resonate with their target audience, drive engagement, and foster trust.
Beyond its analytical capabilities, data analytics serves as a strategic tool for improving CEO communication strategies. By revealing actionable insights, it empowers leaders to refine their communication approaches, thereby enhancing transparency and credibility. In an era where stakeholders increasingly demand transparency and ethical behavior, data analytics not only helps CEOs navigate but also excel in a landscape marked by heightened scrutiny.
We referred to several research papers, blogs posts, scientific articles and tried to list the type of CEO communications used to communicate CSR initiatives.18, 19
The CEO digital communication methods can include the following:
To really make an impact with their communication, companies are increasingly leaning on data analytics and various analytical methods. Let’s explore how some of these methods can be used in different communication scenarios:
By using these analytical methods across various channels, companies can boost their communication strategies, better engage with their audience, and meet their communication objectives.
In this context, we present a comprehensive framework (Figure 1) that combines different modes of CEO CSR communication with specific data analytics techniques. This framework is designed to help organizations enhance their CSR communication efforts, align them with strategic goals, and stay ahead of evolving communication trends. Whether it’s analyzing the sentiment of CEO speeches, tracking the reach of podcasts, or measuring the impact of video messages, data analytics offers valuable insights that drive better decision-making and ultimately contribute to the success of CSR initiatives.
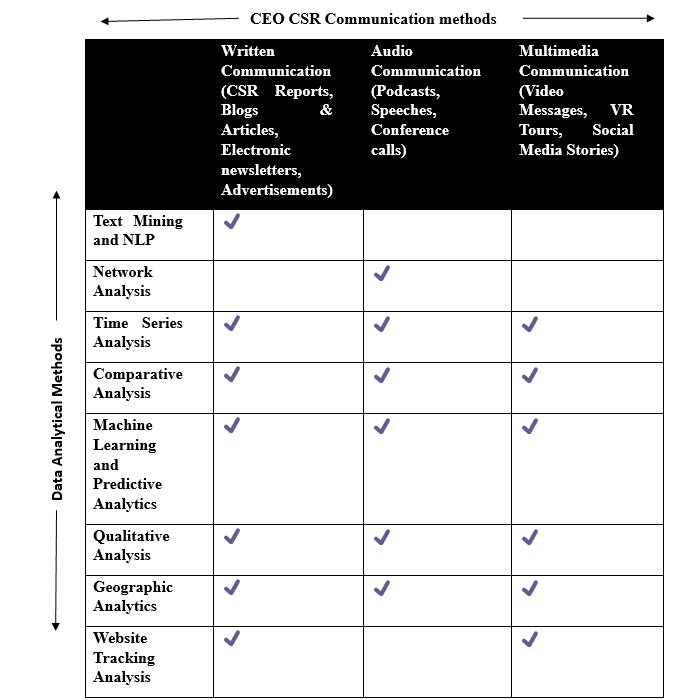 Figure 1 CEO CSR communication analytics framework
Figure 1 CEO CSR communication analytics framework
The practice of using data analytics to analyze CEO Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a crucial approach that holds significant advantages for organizations. CEO CSR analytics entails a systematic evaluation of how a company’s operations impact society and the environment. By thoroughly examining CSR data generated by CEOs, organizations can gain a deep understanding of the effectiveness of their sustainability initiatives and how these efforts influence various stakeholders, including customers, investors, and the wider community.20 This analytical process not only provides a clearer picture of the company’s contributions to society but also enables more informed decision-making, strategic adjustments, and the cultivation of a positive corporate reputation. In a world increasingly focused on sustainability and ethical business practices, embracing CSR analytics is essential for striking a balance between profitability and responsibility.
Analytical approaches for various communication channels is valuable to the organizations. They offer organizations the ability to:
With these analytical approaches at their disposal, organizations can navigate the complex landscape of CEO communication more effectively. It’s about leveraging data to make informed decisions, engage stakeholders, and ultimately, drive positive outcomes for the organization and its mission.
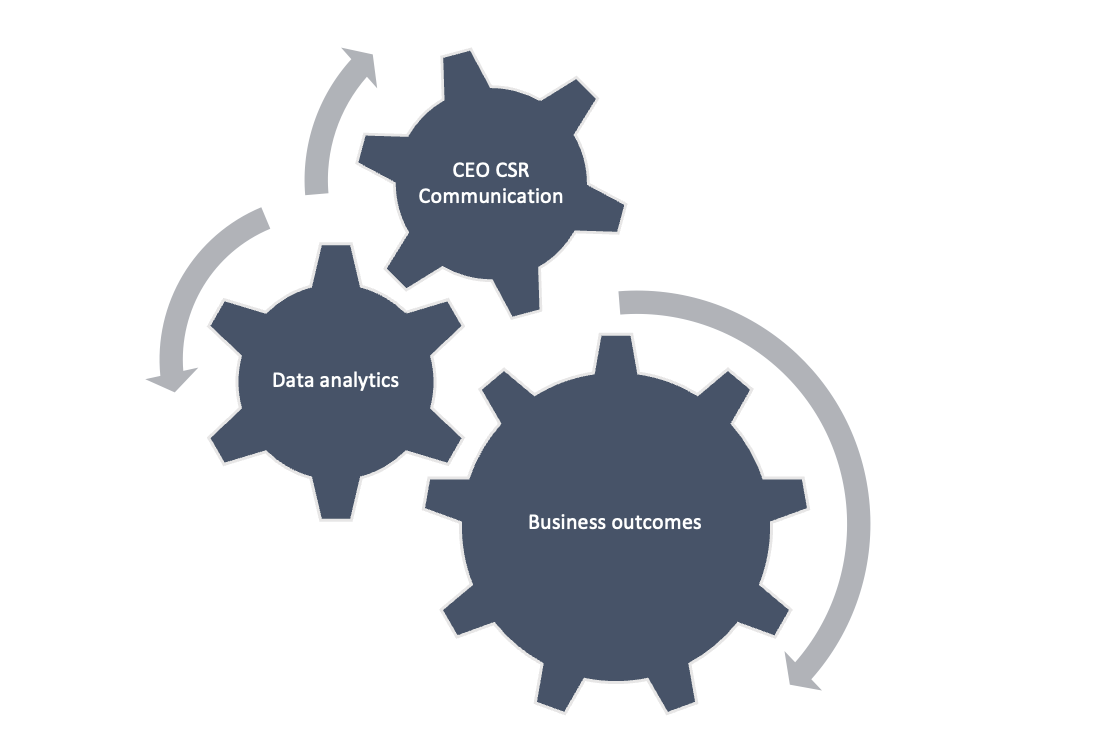
Figure 2 The Strategic CEO Communication Model
The study highlights how important data analytics is in improving the way CEOs talk about Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and its impact on business success (Figure 2). By combining data-driven methods with the subtleties of leadership talk, this approach gives us a clearer view of how executives discuss CSR. This method gives companies the means to really understand the tone and content of CSR communications, which is key to engaging effectively with stakeholders.
Thanks to its flexible nature, this data-driven strategy can be used in various industries. This makes it an essential tool not just for researchers in academia but also for professionals in organizations and those involved in strategic planning. Considering how quickly the business world changes, the framework offered in the study is a reliable way to refine CEO messages and align them better with CSR goals.
Our study doesn’t cover every aspect of CEO communication, all data analytics techniques, or every possible management outcome. However, we’re hopeful that it sets the stage for more in-depth research. We hope that this leads to further investigations into how data analytics can continue to affect and shape CEO communication in the future.
References
Vallaster, C., Lindgreen, A. & Maori, F. Strategically Leveraging Corporate Social Responsibility: A Corporate Branding Perspective. http://dx.doi.org/10.1525/cmr.2012.54.3.34 54, 34–60 (2012).
Cohen, B. & Muñoz, P. Entering Conscious Consumer Markets: Toward a New Generation of Sustainability Strategies. Calif Manage Rev 59, 23–48 (2017).
| Do consumers care about sustainability & ESG claims? | McKinsey. |
2023 Net Positive Employee Barometer FROM QUIET QUITTING TO CONSCIOUS QUITTING. paulpolman.com
New CDP data shows companies are recognizing the need for climate transition plans but are not moving fast enough amidst incoming mandatory disclosure. - CDP.
Grover, P., Kar, A. K. & Ilavarasan, P. V. Impact of corporate social responsibility on reputation—Insights from tweets on sustainable development goals by CEOs. Int J Inf Manage 48, 39–52 (2019).
The Role of Corporate Social Responsibility in 2023: Put Yourself…. movingworlds.org.
How CEOs are prioritizing CSR as central part of corporate vision - Agility PR Solutions.
Furukawa, H. How Does the CEO’s Influence Affect Consumer Brand Trust? The Mediating Effects of Symbolic and Environmental Product Perceptions. https://doi.org/10.1080/08961530.2021.1890299 34, 11–23 (2021).
Grover, P., Kar, A. K. & Ilavarasan, P. V. Impact of corporate social responsibility on reputation—Insights from tweets on sustainable development goals by CEOs. Int J Inf Manage 48, 39–52 (2019).
Jha, A. K. & Verma, N. K. Social Media Sustainability Communication: An Analysis of Firm Behaviour and Stakeholder Responses. Information Systems Frontiers 25, 723–742 (2023).
Raghavendra, A. H., Majhi, S. G., Mukherjee, A. & Bala, P. K. Role of artificial intelligence (AI) in poverty alleviation: a bibliometric analysis. VINE Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Systems (2023) doi:10.1108/VJIKMS-05-2023-0104.
Raghavendra, A. H., Majhi, S. G., Mukherjee, A. & Kumar Bala, P. Australasian Conference on Information Systems 2022, Melbourne Raghavendra et al Artificial Intelligence and Poverty Alleviation Artificial Intelligence and Poverty Alleviation: A Review Research-in-progress.
Li, F., Morris, T. & Young, B. The Effect of Corporate Visibility on Corporate Social Responsibility. Sustainability 2019, Vol. 11, Page 3698 11, 3698 (2019).
Stanislavská, L. K. et al. Global analysis of Twitter communication in corporate social responsibility area: sustainability, climate change, and waste management. PeerJ Comput Sci 9, (2023).
Arvidsson, S. CEO talk of sustainability in CEO letters: towards the inclusion of a sustainability embeddedness and value-creation perspective. Sustainability Accounting, Management and Policy Journal 14, 26–61 (2022).
Elgendy, N., and, A. E.-A. in D. Mining. A. & 2014, undefined. Big data analytics: a literature review paper. Springer 8557 LNAI, 214–227 (2014).
Conte, F., Siano, A. & Vollero, A. CEO communication: engagement, longevity and founder centrality: An exploratory study in Italy. Corporate Communications 22, 273–291 (2017).
Barrett, D. Leadership communication. 428.
 Insight
Anindo Bhattacharjee et al.
Insight
Anindo Bhattacharjee et al.
 Insight
Shaun West et al.
Insight
Shaun West et al.