California Management Review
California Management Review is a premier professional management journal for practitioners published at UC Berkeley Haas School of Business.
by Marco Francesco Mazzù, Rumen Pozharliev, and Irene Della Sala

Image Credit | sergign
The luxury goods industry has recently been under extreme pressure, resulting in several brands experiencing declining economic performance and reputational damage. While anecdotal evidence indicates a shift in consumer attitudes - with younger shoppers perceiving diminished value (Financial Times, 2025) and older consumers affected by fatigue and the trivialization of luxury (Business of Fashion, 2024) - several other factors have proven influential in shaping consumer recent decision-making in the sector. Among these is the interplay of technology-driven engagement modes, which brands are leveraging to meet the expectations of increasingly demanding, conscientious (and fatigued) consumers.
Andreas Kaplan and Michael Haenlein, “To Be or Not to Be: Will Virtual Worlds and the Metaverse Gain Lasting Traction?,” California Management Review, 66/4 (2024): 5-22.
J. Mark Munoz, “AI and Technological Sophistication in Luxury Companies,” California Management Review, Insights (2023).
Unsatisfactory performance and shifting consumer attitudes have brought into question the sufficiency of attributes traditionally associated with luxury in literature, such as exclusivity, quality, and prestige (Dubois & Paternault, 1995; Kapferer & Bastien, 2009). Luxury now faces the challenge of reconciling its hedonistic nature with additional factors, including ethical and environmental principles (Janssen et al., 2017) and technological advancements that are critical for different types of products (Mazzù et al., 2024). Consequently, the luxury sector is undergoing a profound transformation.
Over the past five years, luxury brands have embraced its potential to redefine customer engagement, brand storytelling, and stakeholder relationships, integrating virtual and physical touchpoints to craft immersive experiences (Swaminathan et al., 2020; Kaplan & Haenlein, 2024). Within this context, for example, luxury retailers are enhancing personalized customer engagement through “Luxe Digital” strategies, i.e., advanced technologies like chatbots, machine learning, voice recognition, and image recognition that can support a diverse experience and potentially attract new customer target segments.
In this evolving landscape of digital innovation, the Metaverse has emerged as a transformative paradigm (Hadi et al., 2023), recognized for its potential to foster new forms of engagement and attract new target audiences. Consequently, in recent years, numerous companies have launched pilot projects - each with distinct approaches - to assess their true market potential.
However, despite significant investments in Metaverse technologies aimed at enhancing key brand attributes such as quality, heritage, and authenticity, recent trends indicate a partial reversal, characterized by a progressive disengagement of high-end companies from the Metaverse. This shift is not only due to the current downturn in the luxury market (Davari et al., 2022) and the resulting need to prioritize investments, but mostly due to the absence of a clear model to guide performance outcomes.
The question remains unresolved as to whether the Metaverse can effectively support luxury managers in rebounding their performance.
Drawing on two key research streams - the Value Creation Chain Model (Keller & Lehmann, 2003) and MarTech in Luxury (Kapferer & Bastien, 2009) - this article introduces a conceptual framework linking Metaverse investments to luxury brand attributes, stakeholder engagement, and strategic objectives, ultimately clarifying how high-end brands can reestablish value in this digital frontier through the correct implementation of Metaverse’s strategies. Through the indications derived from an exploratory qualitative research methodology based on 16 in-depth structured interviews with experienced senior executives of top high-end brands from fashion, luxury, automotive and yachting, integrated with evidence from extant research, the proposed model illustrate how the Metaverse can help unlock the full potential of luxury brands in today’s environment. Specifically, it explores how the Metaverse can reinforce, regenerate, access, and engage relevant stakeholders; enhance essential luxury attributes; strengthen relationships with existing customers; and attract new target audiences.
While extensive research has explored digital transformation in luxury, an effective use of the Metaverse to drive luxury business demands a fundamental rethinking of traditional strategies. Literature suggests that customer interactions in this space drive emotional and cognitive engagement, reinforcing brand loyalty and exclusivity. However, challenges such as technological adoption, high implementation costs, and uncertain ROI remain central concerns for luxury executives.
Supported by insights from executives, extant literature and industry research, four defining characteristics of the Metaverse for luxury brands have emerged1:
In the view of top luxury managers, given its multi-layered nature, Metaverse incorporates a range of enabling technologies, each varying in effectiveness in strengthening luxury attributes:
Today, the emergence of the technologies connected to the Metaverse has empowered luxury brands to reinforce and re-generate value for existing consumers by leveraging their traditional luxury and novel attributes, enabling access and favor engagement to new customer groups, and accelerating the sedimentation of heritage and other luxury attributes for new high-end brands aiming to position themselves in the luxury market. Specifically, top executives identified:
Luxury brands initially approached the Metaverse with a “test and learn” strategy, using immersive experiences and exclusive digital offerings to deepen customer engagement and brand loyalty. Progressively, they discovered that beyond existing customers, the Metaverse provides an entry point for aspirational consumers who engage with luxury brands through digital experiences, even if they cannot afford traditional luxury goods (Seo & Buchanan-Oliver, 2015). For instance, these groups of new customers indulge in occasional forays into luxury, such as a belt, a cap or a bag, often reflecting their financial capacity. This expands brand reach and nurtures future high-value customers. Furthermore, the Metaverse has proven effective in engaging a new generation of luxury customers—a specific segment of young, wealthy individuals who are not immediately attracted by traditional luxury cues and attributes. Brands can maintain engagement with this segment through virtual experiences until traditional luxury products become more appealing to them.
Moreover, the research clarified that Metaverse’s impact extends beyond consumers to influence employees, investors, and suppliers:
The potential of the Metaverse to reinforce, re-generate, access, and engage, affects the essential attributes of luxury, impacting the different stakeholders of luxury brands. The presence of a well-executed Metaverse strategy might then deeply affect the brand value creation chain “customer mindset - market performance - shareholder value” (Keller & Lehman, 2003), and the related primary strategic objectives of luxury, encompassing brand equity, customer equity, as well as financial and market performance. In this respect, executives underline diverse areas of the Metaverse’s impact on luxury strategic objectives.
Within the Metaverse, luxury brands can forge strong associations and establish a memorable presence, thereby fortifying their uniqueness and fostering positive perceptions among consumers (Hadi et al., 2023), thus fulfilling objectives of brand equity building, in terms of creating brand assets that contribute positively to the overall value delivered by a product (Aaker, 1996), while generating a differential superior impact on the brand (Keller, 1993). As stated by luxury executives “if you aim to establish a brand presence in the metaverse, it is essential to adopt a long-term perspective on its activation and to cultivate users’ trust over an extended period. Building a sustained presence allows for the gradual development of visibility and awareness within the metaverse community. This strategic approach ensures that the brand becomes a trusted entity, contributing to its lasting impact and resonance in the Metaverse space”. Notably, the application of reality enhancement technologies like VR, AR, and MR in the luxury sector affects the customer journey and contributes to strengthening brand equity (Javornik et al., 2021; Buhalis et al., 2022).
By leveraging extended-reality technologies and gamification, brands can deepen emotional connections, reinforce exclusivity, and cultivate customer loyalty. Brands that successfully navigate the Metaverse will secure a competitive edge, ensuring long-term adaptability in an evolving digital market. However, for sustained success, luxury brands must focus on three critical enablers:
Figure 1. Integrated model of the impact of Metaverse on the luxury industry
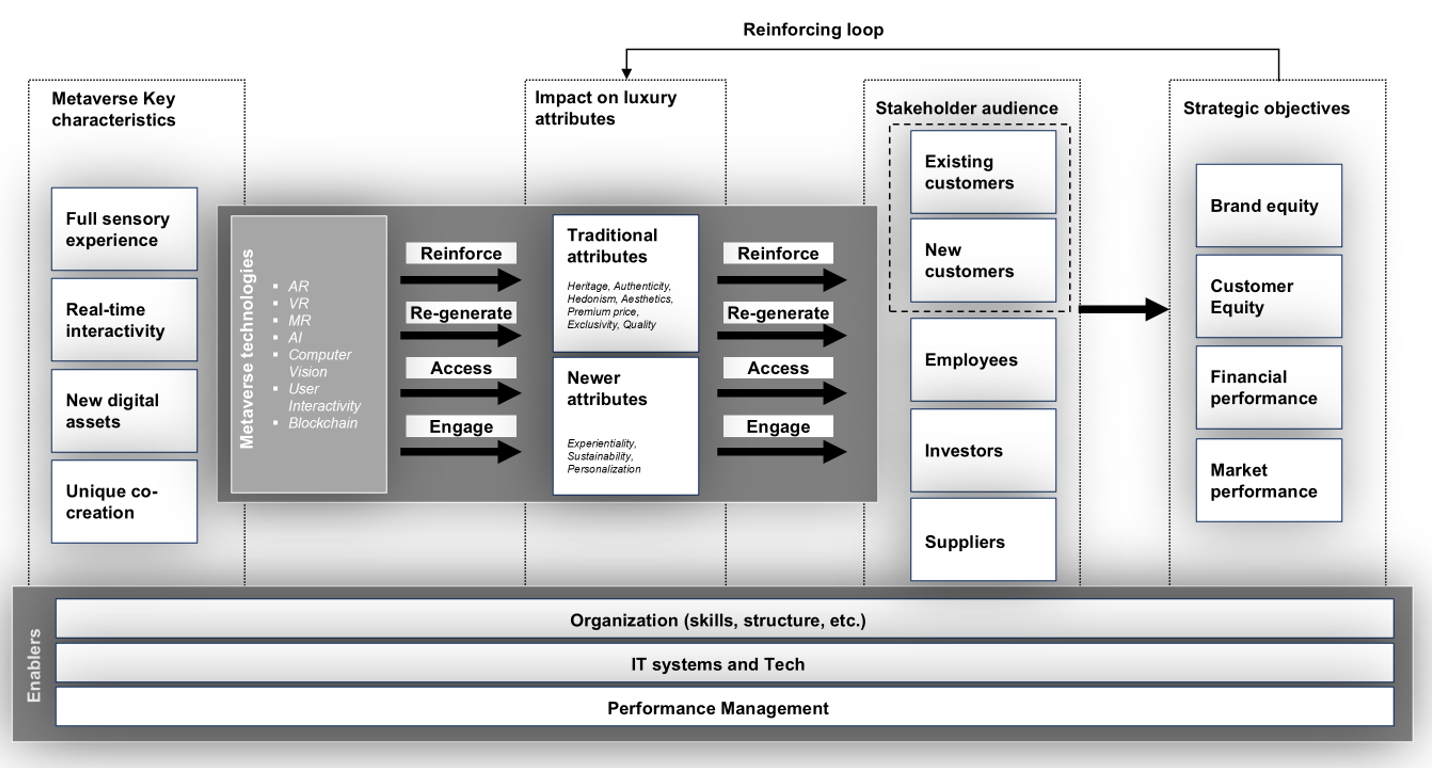
Our research highlights the Metaverse’s transformative potential for luxury brands, offering new ways to engage consumers, boost heritage, and drive financial performance. By relying on a set of structured in-depth interviews, our research shows that luxury brands can leverage the Metaverse to reinforce, re-generate, access, and engage relevant stakeholders, by positively affecting a relevant set of luxury attributes. This enables brands not only to strengthen relationships with existing customers but also to embrace new communities and target audiences. Once luxury attributes are aligned with the Metaverse, brands may experience a positive impact on their strategic objectives, provided that specific enablers are in place. Therefore, once the above is set, a significant effect might be expected in strengthening brand and customer equity, improving company performance, and creating the basis for a reinforcing loop.
However, Metaverse adoption follows a three-phase progression, reflecting different implementation and readiness horizons among luxury brands:
Figure 2. Metaverse’s KPIs and business horizons
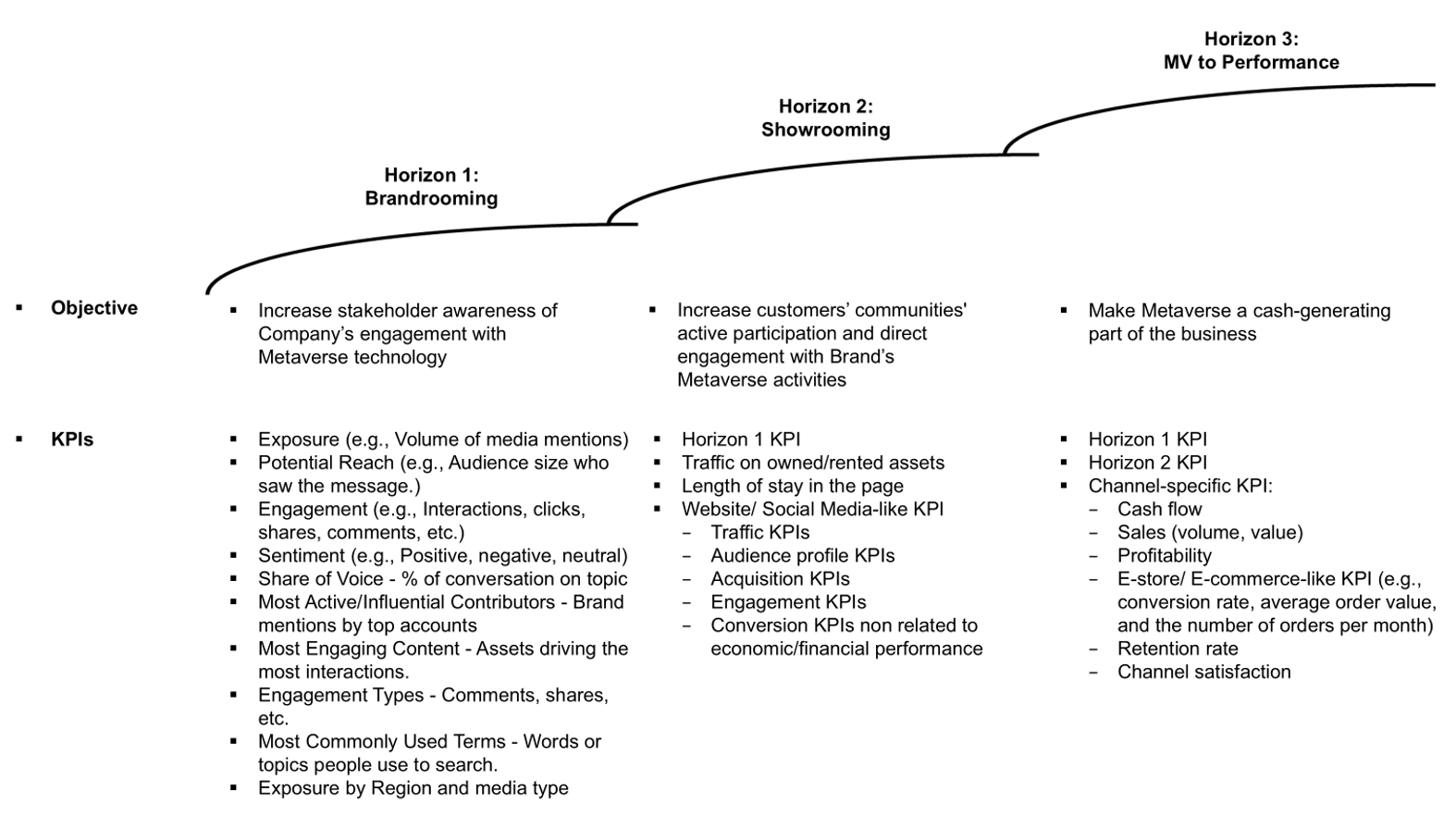
As the digital landscape evolves, luxury brands must refine their Metaverse strategies to align with changing consumer behaviors and technological advancements. While challenges remain, brands that effectively integrate Metaverse technologies will be best positioned to shape the future of luxury, maintaining exclusivity and innovation in an increasingly digital world.
To restore the growth trajectories experienced in the last decade, a prominent role will then be played by the growing interest among stakeholders in how luxury companies address various facets of technology advances — and specifically the most discontinuous ones as the Metaverse – as a core element in shaping branding strategies to remain competitive within the sector.
[1] In italics are present excerpts from interviews with top executives of luxury companies